Astrobiology is a field of science that seeks to understand the nature of life in the universe. It brings together researchers from a variety of disciplines, including astronomy, biology, chemistry, and geology, to study the origins, evolution, and distribution of life beyond our planet.
One of the main goals of astrobiology is to identify and explore the potential for extraterrestrial life. By studying the characteristics and requirements of life on Earth, scientists can develop hypotheses about what kinds of environments and conditions might be suitable for life to exist elsewhere in the universe.
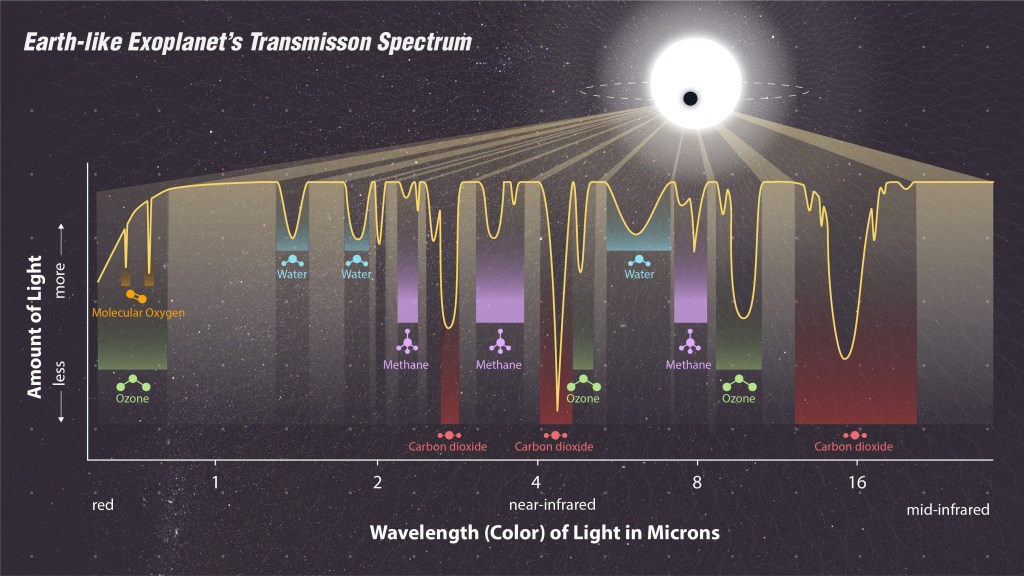
While astrobiology is a relatively new field, it has already yielded some fascinating discoveries. For example, the discovery of exoplanets – planets orbiting stars other than our sun – has opened up new avenues for exploration and research. Scientists use a variety of techniques to study these exoplanets, including analyzing their atmospheres for signs of life-sustaining gases such as oxygen and methane.
As our understanding of the universe continues to grow, so too does our ability to explore the possibility of extraterrestrial life. While we may not yet have definitive answers to the question of whether life exists elsewhere in the universe, the field of astrobiology offers a tantalizing glimpse into the that await us.
Conditions for Habitability
Location
The habitable zone, sometimes referred to as the “Goldilocks zone,” is a region around a star where the conditions are just right for the possibility of life. Planets that fall within this zone are neither too close nor too far from their star, which means they receive just the right amount of energy to maintain a temperature that can support liquid water on their surface. Water is essential for life as we know it, so the presence of liquid water greatly increases the chances of finding living organisms beyond our own world.
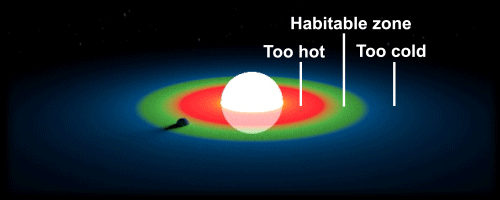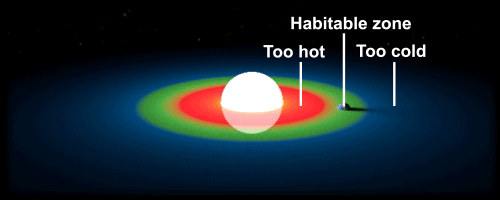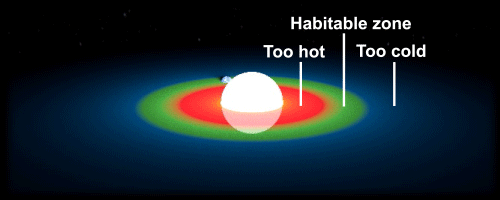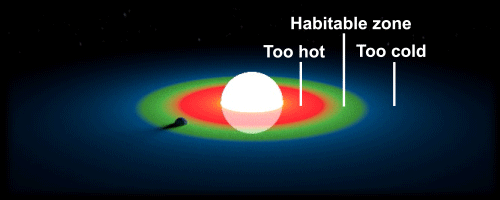
Of course, the habitable zone is just one of many factors that can influence the potential for life on a planet. Other factors, such as the presence of a protective atmosphere or magnetic field, can also play a critical role in making a planet habitable. Nevertheless, the habitable zone remains a useful concept for identifying planets that offer the best chance of finding life as we know it.
Atmosphere
Life as we know it relies on a delicate balance of environmental factors, many of which are provided by the surrounding atmosphere. One key function of the atmosphere is to protect living organisms from harmful radiation. Earth’s atmosphere, for example, contains a layer of ozone that absorbs much of the sun’s ultraviolet radiation before it can reach the surface.
In addition to providing protection from radiation, the atmosphere also plays a critical role in regulating temperature. Without the greenhouse effect caused by certain atmospheric gases, such as carbon dioxide and water vapor, Earth’s average temperature would be far too cold to support most forms of life.
Of course, the specific atmospheric conditions required to support life can vary widely depending on the organism in question. Some extremophiles, for example, are capable of surviving in environments that would be deadly to most other forms of life. Nevertheless, the atmosphere remains a key factor in determining the habitability of a planet or other celestial body.
Chemistry
The presence of complex organic compounds, such as amino acids and nucleotides, is essential for life as we know it. These molecules serve as the building blocks of proteins, DNA, and other biomolecules that are necessary for living organisms to function.
The formation of these complex organic compounds can occur through a variety of processes, both natural and synthetic. In some cases, these compounds may have originated from the primordial soup of early Earth, where conditions were ripe for chemical reactions to occur. In other cases, complex organic compounds may be synthesized in the laboratory or other controlled environments.
Regardless of their origin, the study of complex organic compounds is a critical area of research in the fields of biology, chemistry, and astrobiology. By understanding the chemical processes that give rise to these molecules, scientists can better understand the origins and evolution of life on Earth and beyond.
Search for Extraterrestrial Life
Scientists are constantly searching for signs of life beyond our own planet. To do this, they use a variety of methods and tools.
One approach is to analyze the atmospheres of exoplanets, or planets outside our solar system, for bio-signatures. These are gases that could be produced by living organisms, such as oxygen or methane, and could indicate the presence of life on the planet.
Another method involves exploring the chemical pathways that lead to the formation of prebiotic molecules, or the building blocks of life. By understanding how these molecules can form, scientists can better understand the conditions that may have led to the emergence of life on Earth and other planets.
Finally, some scientists search for intelligent civilizations by listening for radio signals from space. This approach, known as the search for extraterrestrial intelligence (SETI), involves scanning the cosmos for signals that could be produced by other technological civilizations.
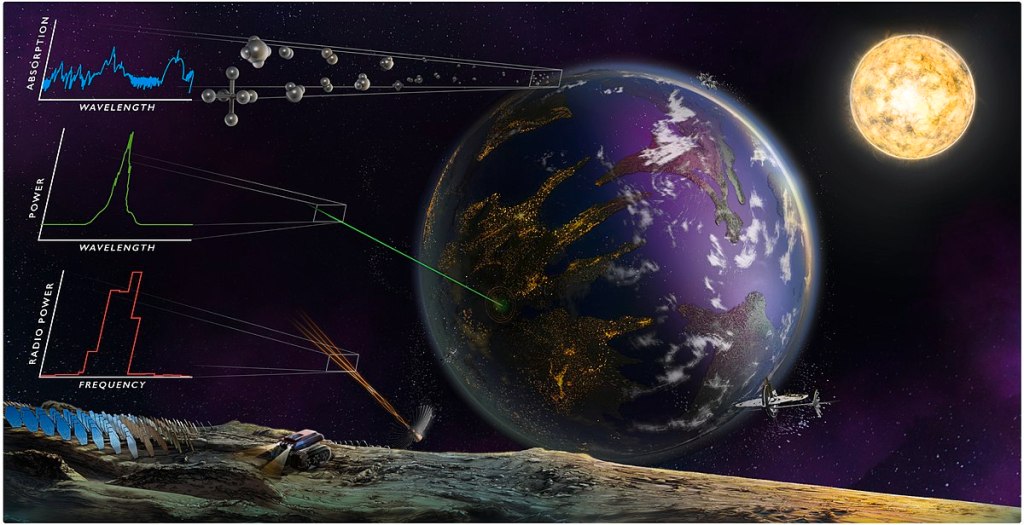

With all these methods at their disposal, scientists remain hopeful that we will one day discover evidence of life beyond our own planet.
Potential exoplanets that could host life
| Name | Distance from the Sun | Mass | Total Number of Planets in the System |
| Proxima Centauri b | 4.2 light years | 1.3 Earth masses | 1 |
| Kepler-452b | 1,400 light years | 5 Earth masses | 1 |
| TRAPPIST-1e | 39 light years | 0.62 Earth masses | 7 |
Exoplanets are planets that orbit stars other than our sun. Several exoplanets have been discovered to be within their star’s habitable zone. Scientists are exploring their potential for extraterrestrial life.
Extremophiles and Their Role in Astrobiology
Extremophiles are a fascinating group of organisms that have captured the attention of scientists around the world. These creatures are known for their ability to thrive in extreme environments, such as hot springs, deep-sea hydrothermal vents, and even in space.
Studying these organisms provides valuable insights into the limits of life on Earth, and offers clues into the potential for life in seemingly inhospitable environments elsewhere in the universe. For example, the discovery of extremophiles in the deep sea has led scientists to speculate about the possibility of life on other planets, such as those with subsurface oceans.
Extremophiles come in many different forms, from bacteria and archaea to fungi and even some animals. Some are able to withstand extreme temperatures, while others can survive in highly acidic or alkaline environments. Still others are adapted to extreme pressure, radiation, or desiccation.
Despite their remarkable abilities, extremophiles face many challenges in their extreme habitats. For example, they must contend with limited resources, high levels of toxicity, and intense competition from other organisms. Nevertheless, these creatures have managed to adapt and thrive in some of the most inhospitable places on Earth, inspiring scientists to continue exploring the limits of life and the potential for finding it elsewhere in the universe.

Halophiles: These organisms thrive in highly saline environments, such as the Dead Sea and salt flats.
Thermophiles: These organisms can survive in extremely high temperatures, such as hot springs and deep-sea hydrothermal vents.
Cryophiles: These organisms can survive in extremely low temperatures, such as the ice caps of Antarctica.
Future of Astrobiology Research
As technology advances, astrobiology research will continue to develop new and exciting methods of studying the origins and distribution of life in the universe.
One approach is to explore the subsurface oceans of icy moons, such as Europa, Enceladus, and Titan. These moons are believed to have liquid water oceans beneath their icy surfaces, which could harbor life. Future missions to these moons, such as NASA’s Europa Clipper, aim to study their oceans and search for signs of life.

Another method involves studying the atmospheres of exoplanets, or planets outside our solar system. By analyzing the gases in their atmospheres, scientists can look for bio-signatures, or gases that could be produced by living organisms. For example, oxygen and methane are both potential bio-signatures that could indicate the presence of life on an exoplanet.
Finally, some scientists are exploring the potential for life in other parts of our own solar system, such as Mars and the icy moons of Saturn and Jupiter. These bodies may have once had habitable conditions, and could still harbor life in subsurface oceans or underground aquifers.
With all these methods at our disposal, the possibilities for astrobiology research are truly endless. By continuing to push the boundaries of technology and exploration, we may one day discover that we are not alone in the universe.
Implications for Humanity
Scientific
Exploring the Origins of Life on Earth and Beyond
The study of astrobiology is a multidisciplinary field that seeks to understand the origins and evolution of life in the universe. By investigating the conditions that led to the emergence of life on Earth, astrobiologists hope to uncover clues about the potential for life on other planets and moons in our solar system and beyond.
One of the key questions in astrobiology is how life originated on Earth. Scientists believe that life on our planet emerged from a combination of complex chemical reactions that took place in the primordial soup of Earth’s early oceans. By studying the properties of early Earth and the chemical processes that occurred there, astrobiologists hope to gain insights into the conditions that might be necessary for life to arise on other worlds.
In addition to studying the origins of life, astrobiologists are also interested in understanding how life has evolved over time. By examining the fossil record and using genetic and molecular techniques, scientists can trace the history of life on Earth and learn about the diversity of life that exists on our planet today. These insights could help us identify signs of life on other worlds, even if that life is radically different from what we see on Earth.
Technological
Applications of Astrobiology Research
The study of astrobiology has the potential to revolutionize our understanding of the universe and to inspire new technologies and innovations. One of the most exciting aspects of astrobiology research is the way it can lead to new breakthroughs in fields such as medicine, energy, and environmental science.
Medicine
Many of the technologies and techniques developed for astrobiology research have direct applications in the field of medicine. For example, researchers studying the effects of radiation on organisms in space have developed new methods for protecting astronauts from radiation exposure. These same methods could also be used to develop new treatments for cancer and other radiation-related illnesses.
Energy
Another area where astrobiology research is making an impact is in the search for new sources of energy. Scientists studying the formation and evolution of planets and moons are discovering new insights into the geology of these bodies and the processes that shape their surfaces. By using this knowledge to identify new sources of minerals and ores, astrobiologists are helping to create a more sustainable future for our planet.
Environmental Science
Astrobiology research is also contributing to our understanding of the Earth’s environment and the effects of climate change. By studying the history of the Earth’s climate and the ways in which it has changed over time, astrobiologists are helping to develop new strategies for mitigating the effects of global warming and preserving the planet for future generations.
Philosophical
The discovery of extraterrestrial life could have profound implications on our understanding of the universe and our place within it.
For centuries, humans have looked up at the stars and wondered if we are alone in the universe. The discovery of even the simplest forms of life beyond Earth would revolutionize our understanding of the cosmos, and could potentially answer some of the biggest questions in science, such as how life originated and what the ultimate fate of the universe will be.
Moreover, the discovery of extraterrestrial life could have important philosophical, religious, and societal implications. It could challenge our beliefs about the uniqueness of human life, and force us to rethink our place in the universe. It could also have practical implications, such as inspiring new technologies and space exploration missions.
Despite decades of searching, we have yet to find definitive evidence of extraterrestrial life. However, with advances in technology and new exploration missions on the horizon, the possibility of discovering life beyond Earth seems more promising than ever before.
“Exploration is in our nature. We began as wanderers, and we are wanderers still. We have lingered long enough on the shores of the cosmic ocean. We are ready at last to set sail for the stars.”
– Carl Sagan
The universe is a large place, and there are many things we do not yet know. But one thing is certain: the search for knowledge will continue, and it will not stop until we find the answers we seek.
From the tiniest particles to the largest galaxies, there is so much to discover about the world around us. Scientists, explorers, and thinkers of all kinds are constantly pushing the boundaries of what we know, asking new questions and seeking new insights.
While we may never have all the answers, the journey of discovery is one that we can all take part in. Whether through scientific research, artistic expression, or simply observing the world around us with curiosity and wonder, there is always something new to learn and discover.
So let us continue on this journey of discovery together, always asking questions, seeking answers, and pushing the boundaries of what we know.
